Gabor Zavodszky co-authored an article in Cardiovascular Engineering and Technology.
For more information read below, or click the following link: https://rdcu.be/bYivL
Purpose
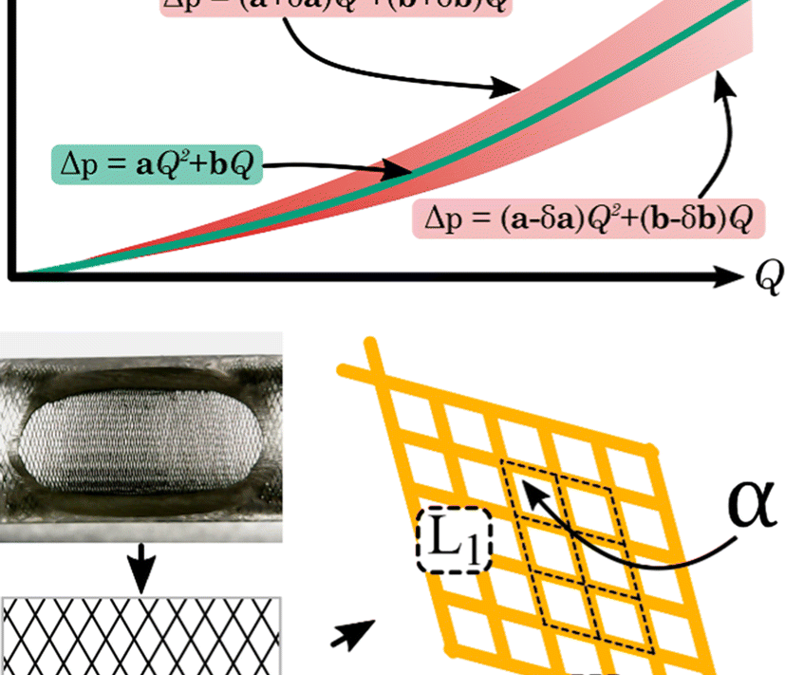
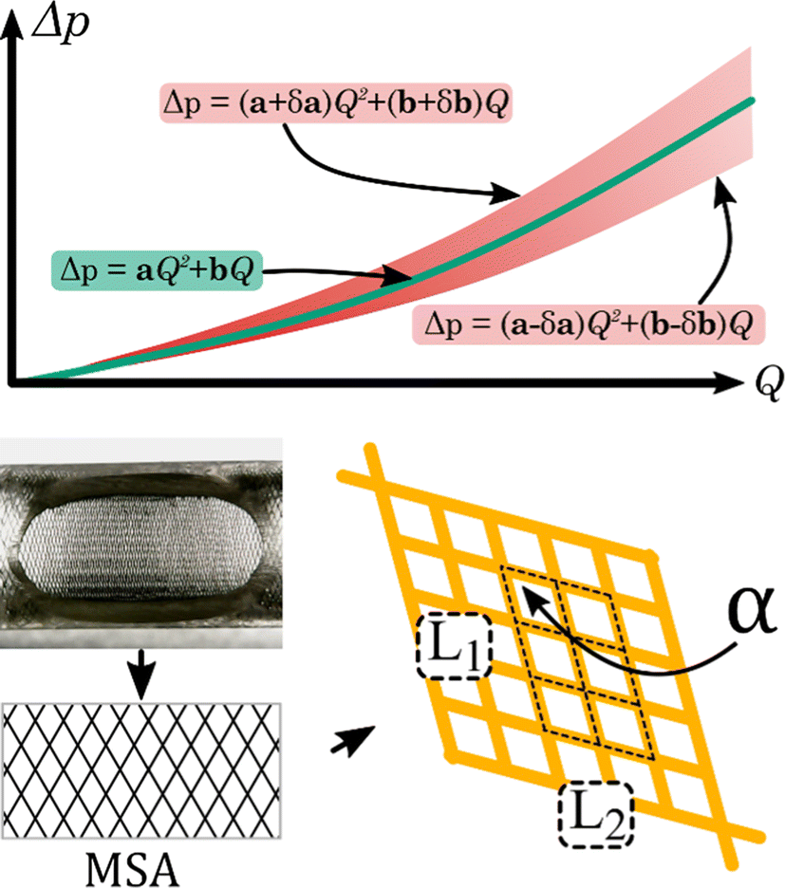
Intracranial aneurysms are malformations forming bulges on the walls of brain arteries. A flow diverter device is a fine braided wire structure used for the endovascular treatment of brain aneurysms. This work presents a rig and a protocol for the measurement of the hydrodynamic resistance of flow diverter stents. Hydrodynamic resistance is interpreted here as the pressure loss versus volumetric flow rate function through the mesh structure. The difficulty of the measurement is the very low flow rate range and the extreme sensitivity to contamination and disturbances.
Methods
Rigorous attention was paid to reproducibility, hence a strict protocol was designed to ensure controlled circumstances and accuracy. Somewhat unusually, the history of the development of the rig, including the pitfalls was included in the paper. In addition to the hydrodynamic resistance measurements, the geometrical properties—metallic surface area, pore density, deployed and unconstrained length and diameter—of the stent deployment were measured.
Results
Based on our evaluation method a confidence band can be determined for a given deployment scenario. Collectively analysing the hydrodynamic resistance and the geometric indices, a deeper understanding of an implantation can be obtained. Our results suggest that to correctly interpret the hydrodynamic resistance of a scenario, the deployment length has to be considered. To demonstrate the applicability of the measurement, as a pilot study the results of four intracranial flow diverter stents of two types and sizes have been reported in this work. The results of these measurements even on this small sample size provide valuable information on differences between stent types and deployment scenarios.